Uptime is the amount of time a website is up and running without interruptions. Web hosting companies measure uptime as a percentage of the total possible time a website can be online. The results can show how reliable or unreliable a hosting service is.
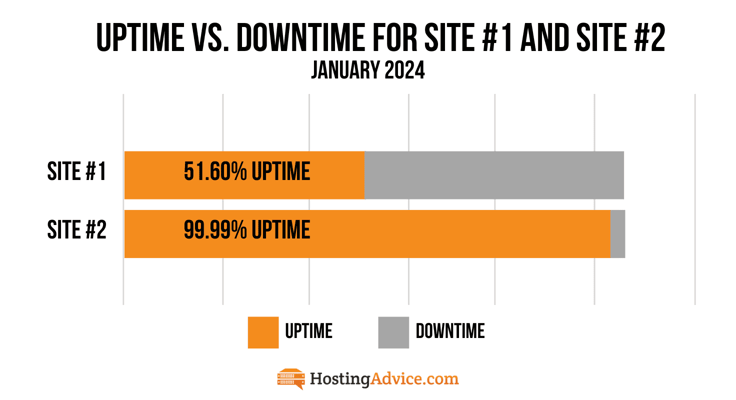
Industry uptime standards are pretty high. While 99% uptime may sound good, it really means your site could be down for 3.65 days a year — a situation that could lead to disastrous business outcomes.
In contrast, high uptime would be something like 99.9% or greater. This coincides with roughly 8.7 hours of downtime per year, a much more palatable amount. This guide will take you through the ins and outs of uptime, including its importance, factors that impact it, and how you can maximize it.
-
Navigate This Article:
Understanding the Importance of Uptime
Let’s begin by taking a deeper look at uptime, what it’s all about, and why it’s really important in the web hosting space. Once that’s out of the way, we’ll touch on how we measure and report uptime, what tools to use, and what to do with the information we gather from these tools.
Uptime vs. Downtime: What’s the Difference?
Uptime and downtime are opposites when it comes to system availability. Uptime refers to the amount of time a system is online, and downtime refers to the amount of time a system is offline.
How Uptime Is Measured and Reported
Web hosting companies measure uptime using a percentage. An uptime of 99.9% is the most common since it’s considered the industry standard. This percentage represents how often a website or service stays available and functioning over a specific period, like a month or year.
You can measure uptime through server monitoring tools (more on that below). These tools continuously check the website’s availability by simulating visits or pinging the server to see if it responds.
Web hosting providers, particularly reliable ones, usually report uptime in their service level agreements (SLAs). In an SLA, the web host promises you, the client, a certain standard of service. The percentages mentioned in the SLA can vary. However, to be on the safer side, you need an uptime guarantee of 99.9% or higher.
Significance of Uptime for Business Success
Uptime is something you simply can’t overlook when running an online business. It impacts your credibility, revenue, user experience, and search engine rankings.
A small amount of downtime won’t tank your SEO efforts, but Google will penalize your site for consistent downtime. Frequent downtime also creates user dissatisfaction. If potential customers encounter repeated errors when visiting your website, they aren’t likely to return.
In contrast, high uptime offers many benefits for your business. Some of these include a professional image and an uninterrupted user experience. Both of these factors can increase your conversion rate and turn site visitors into customers.
The Impact of Uptime on Site Performance
Let’s now look at how uptime impacts website performance, specifically in these three areas: user satisfaction, website accessibility, and search engine rankings.
Importance of 99%+ Uptime for User Satisfaction
Consistent uptime ensures that your website is always available when users need it. Your site constantly being down is a sure way to frustrate your visitors.
Sooner than later, the frustration will lead to a poor user experience and eventual exit from the site. So much so that 79% of online shoppers would not revisit a site with a poor user experience — don’t let your website fall prey to this statistic.
Relationship Between Uptime and Site Availability
As we mentioned at the beginning of this article, uptime is the amount of time your website stays up and running. Uptime and availability go hand-in-hand. If a website has high uptime, that means it also has a high level of availability.
Availability is a measure of how reliable your website is for site visitors. You need both high uptime and high availability to have a successful website.
Influence of Uptime on Search Engine Rankings
Search engines like Google and Bing would rather direct users to sites with high uptime and availability than those with significant downtime. When search engine bots crawl your site during a period of downtime, they collect that information.
Now, depending on how frequently this happens, your search engine rankings could begin to tank. Eventually, your site’s visibility on search engines will suffer. And you can’t really blame search engines for the drop in rankings. Unavailable content is not helpful to search engine users.
Impact of Downtime on Revenue and Brand Reputation
Perhaps the best way to understand how critical uptime is to a business is by looking at Amazon.com. In the first quarter of 2021, the eCommerce giant reportedly made about $830,000 per minute in revenue.
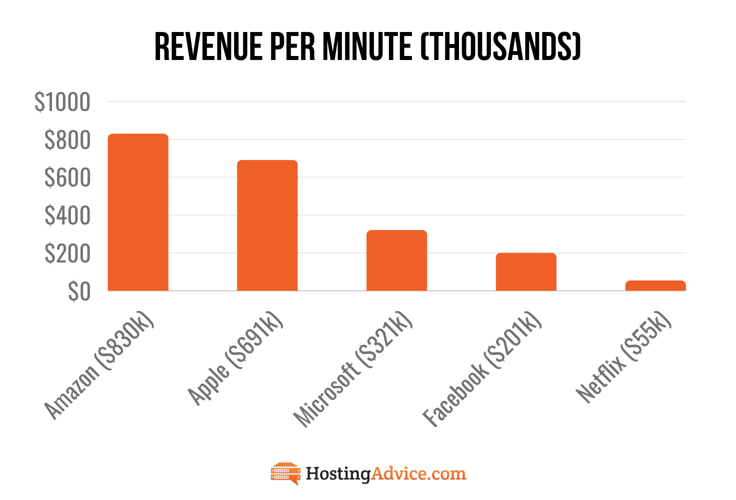
You can imagine how three minutes of downtime would impact a business like Amazon. To give you some perspective, we’re looking at a loss of about $2,490,000 million in three minutes!
Not only does downtime impact revenue, but it also affects a brand’s reputation. If an eCommerce platform started experiencing widespread unavailability, shoppers would soon turn to more reliable online retailers.
What Factors Affect Uptime?
If uptime was a machine, different cogs and wheels would need to work together to make the machine run optimally. To explain this further, we’ll briefly review some of the factors that could affect uptime.
1. Server Reliability and Infrastructure Quality

Powerful, well-maintained servers are less likely to fail. The same applies to a well-designed infrastructure with redundancy, such as multiple power sources and backup systems. Such infrastructure ensures that the website remains operational even if one part of the system fails.
For example, data centers with backup generators and redundant cloud networks are likely to have greater uptime than a single on-premise server.
2. Network Connectivity and Bandwidth Availability

The network should have enough bandwidth to handle traffic to and from the server easily.
Without this, any user connected to that network will likely experience slow load times or server outages.
Internet service providers (ISPs) and hosting providers must make sure that their network infrastructure can scale with increased demand.
But that’s not all; the infrastructure should be able to withstand and fight DDoS attacks or hardware failures.
3. Maintenance and Update Management

Hosting companies should conduct regularly scheduled maintenance for their servers and software.
This process ensures that servers are up to date and running optimally, preventing unexpected breakdowns.
There is no doubt that regular server maintenance is one way to maintain uptime, but how you do it matters, too.
For example, it’s generally good practice to roll out updates in a controlled, staged manner to avoid disruptions.
4. Security Measures Against Cyber Threats

Lastly, it’s common knowledge that cyberattacks can lead to downtime.
Implementing strong security protocols like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits can help mitigate these risks.
The host should also educate its staff about security best practices and how to implement tested recovery plans in the event of a security breach.
Uptime Monitoring and Management
You need to implement certain strategies to achieve high uptime, including the use of monitoring tools and management protocols. Let’s take a closer look at what these strategies entail.
Introduction to Uptime Monitoring Tools and Services
One great way to monitor uptime is to use tools such as Better Stack, Pingdom, UptimeRobot, StatusCake, and Site24x7. These services continuously check a website’s availability by regularly sending requests to the server and recording the responses.
If a site is unreachable or returns an error, the monitoring service alerts the site administrators. This process helps site admins address potential issues promptly, minimizing the chances of downtime.
Later in this article, I’ll demonstrate how uptime monitoring works by setting up a monitoring environment with Better Stack. Speaking of monitoring, you have two options here: synthetic and real user monitoring. We’ll dive into the differences below.
Synthetic vs. Real User Monitoring
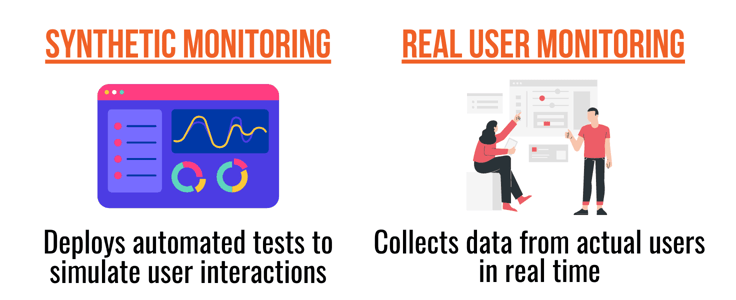
Synthetic monitoring is when you deploy automated tests to a website from various locations to simulate user interactions. This strategy can help detect downtime and performance issues before they begin to affect real users.
On the other hand, real user monitoring is exactly what it sounds like. Here, you collect data from actual users in real time. This user data will reveal how users interact with the website under natural traffic conditions.
So, why would you opt for any of these methods? It’s because they both have their own unique benefits.
Synthetic monitoring is more of a proactive and controlled approach. This method gives you an idea of what would happen if something went wrong with the website. That way, you’ll know how to prevent these events before they happen.
Real-user monitoring works best when you want to monitor a real-life situation. Unlike synthetic monitoring, which uses fake users, real user monitoring is more accurate and shows what an actual site visitor experiences.
You can also use uptime robots to check the availability of websites by pinging them at regular intervals, usually every five minutes. If the tool detects downtime, it notifies the website administrators via email, SMS, or other configured methods.
Setting up Uptime Monitoring for Websites
To further demonstrate how uptime monitoring works, we’ll use Better Stack (formerly known as Better Uptime), a popular uptime monitoring tool. While this tool also offers premium features, the free version is good enough for demonstration purposes.
You’ll first need to set up a free account with Better Stack. Head over to its website, enter your email address, and click Start in 30 seconds.
Go to your email inbox, open the confirmation email from Better Stack, and then click Set up your account.

Fill out the signup form on the next page. Remember to enter the URL of the website you want to monitor. You can also enter your phone number to receive SMS notifications about your website’s uptime status.
Keep in mind that you do not need your credit card information to complete the signup process; you can always choose the free plan. Once you’ve accessed the website’s dashboard, you’ll see a full report of the website’s performance, as shown below.
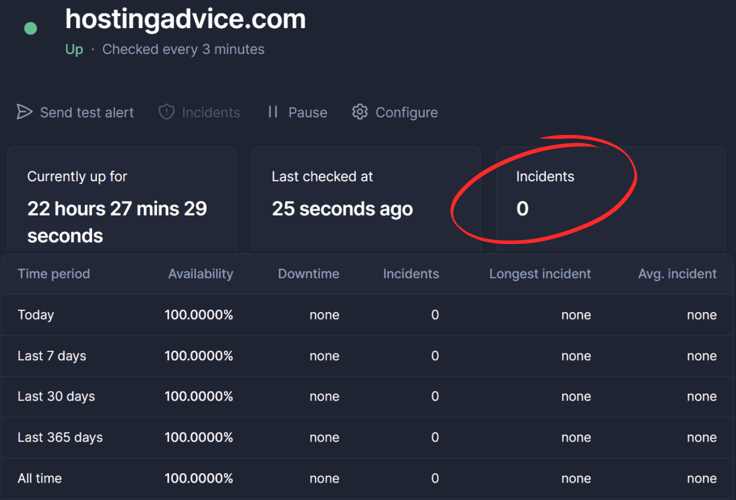
The report above gives you all the information you need about your website’s uptime. It includes the latest downtime incidents, the average uptime rate, timestamps of routine uptime checks, and so much more.
Interpretation of Uptime Reports and Metrics
After collecting uptime reports and metrics, the next step involves analyzing data. The whole point of this step is to understand the availability and reliability trends of your website.
Some of the most important information in these reports include uptime percentages, response times, and the history of downtime incidents. By examining these metrics, web or server administrators can identify recurring issues, assess the impact of performed optimizations, and make better, data-driven decisions about improving overall user experience.
Strategies for Uptime Management and Optimization
Taking a proactive approach to uptime management means always being one step ahead in preventing downtime and boosting performance. This is made possible by:
- Using backup hardware and network setups that prevent any single point of failure.
- Spreading traffic evenly across multiple servers, a tactic commonly referred to as load balancing in the web hosting space.
- Keeping all essential systems up to date with regular updates and patches.
- Conducting thorough capacity planning and performance testing to anticipate and tackle any potential bottlenecks before they impact the user experience.
With the strategies outlined above, websites can remain consistently reliable and quick to respond, no matter the situation.
Best Practices for Ensuring High Uptime
You should consider adopting a series of best practices that keep your services running smoothly and efficiently. Let’s dive into some key strategies that can help you maintain an excellent online presence.
Choosing a Reliable Web Hosting Provider
Choosing the right web hosting provider is like choosing a dependable partner — it’s a decision that will impact every aspect of your website’s performance. You need a host that not only offers great uptime guarantees but also backs them up with actual performance data.
Make sure your host has a powerful hosting infrastructure and provides excellent customer support. It goes without saying that a reliable host is your first defense against downtime.
Implementing Redundancy and Failover Mechanisms
You need to set up additional systems that can smoothly swing into action in case something goes wrong with your main setup. We’re talking about extra servers and alternative power sources or even multiple data centers.
That way, there’ll be no service interruption. If system “A” fails, system “B” takes over immediately. In the meantime, you’ll be working on fixing system “A” and finding ways to prevent such issues from reoccurring.
Regular Maintenance and Updates to Prevent Downtime
You should also stay on top of maintenance and updates to avoid unexpected downtime. One way of doing this is by regularly updating your software.
Consider scheduling planned maintenance. But remember to do this during off-peak hours and after alerting users about the scheduled maintenance.
I’m pretty sure you’ve seen such alerts on various websites or applications you interact with daily. Your bank, for example, may send out something like:
“Our internet banking services will be unavailable for routine maintenance from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM Sunday 4/21/2024. We apologize for the inconvenience.”
This strategic timing and advance notice minimizes the impact on your users and keeps everyone informed about when to expect brief service disruptions.
Monitoring and Addressing Performance Issues Promptly
Keep a close eye on your website’s performance. This proactive approach helps you spot and address potential issues before they escalate into bigger problems.
By reacting swiftly to performance dips, you maintain a more reliable user experience. That way, you’ll keep visitors happy and reduce stress on your end, creating a win-win scenario as a result.
Disaster Recovery Planning and Backup Solutions
Finally, you need a solid disaster recovery plan and reliable backup solutions to prepare for the unexpected. Regular backups are non-negotiable — they allow you to restore services quickly after an incident.
Comprehensive disaster recovery planning is one essential strategy for preparing and responding effectively to any scenario. This solution not only prevents downtime but also keeps your data protected from parties with bad intentions.
Uptime Guarantees and SLAs
When selecting a web hosting service, you should understand the uptime guarantee and service level agreement (SLA) it offers. These are commitments that provide a clear expectation of service reliability. They also outline the recourse if the provider doesn’t meet these pre-agreed expectations. Here are some important things to know.
Uptime Guarantees Offered By Hosting Providers

Many top-tier hosting providers offer impressive uptime guarantees, typically ranging from 99.9% to 99.9999%. Note that these percentages are a direct reflection of the availability of your servers.
Take, for instance, a 99.99% uptime guarantee. This means your site should only experience about 52 minutes of downtime annually. On the other hand, a 99.999% uptime pushes that down to just 5 minutes annually.
Providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure are renowned for such high standards. The secret? It all boils down to their extensive redundant infrastructure and cutting-edge web hosting technologies.
Service-Level Agreements

As revealed earlier, SLAs are formal documents that outline the specifics of uptime guarantees. They also set the expectations for service provision.
By “expectations,” we mean how these hosts manage downtime and communicate it to customers. SLAs ensure that hosting providers are held accountable for maintaining the agreed-upon level of service.
They function as an agreement between the client and the web hosting provider. The provider promises to maintain a certain standard if the client agrees to sign up for that particular web hosting plan.
In these agreements, you’ll find details on how web hosting providers will notify customers during outages and the compensation customers may be entitled to for unexpected downtime.
The whole point of having SLAs is to provide assurance and transparency. These qualities can help build trust between the service provider and the customer.
Pro Tip: Evaluating the Reliability of Uptime Guarantees
Almost every web host has some form of uptime guarantee. But how credible are they? Spoiler alert: don’t believe every uptime guarantee you see. Some hosts, particularly free ones, may not live up to the advertised uptime. Review the SLA carefully to see if the provider backs its statements.
You’ll need to scrutinize the hosting provider’s track record and the strength of its infrastructure. Reading independent web hosting reviews is a good place to start. But that’s not all there is to it.
Look for web hosting providers with transparent access to performance data and third-party audit results. Case studies can also provide insight into how frequently the provider meets its uptime promises and how it handles exceptions.
Uptime Optimization Strategies
Now, let’s go over some proven technical approaches that can ensure that your website stays online and delivers the best possible user experience.
Load Balancing and Traffic Distribution
Load balancing involves distributing incoming web traffic across multiple servers. As a result, no single server bears too much load, which could lead to downtime.
Think of it as a traffic cop directing cars at an intersection. The traffic cop, or load balancer, keeps things moving by directing traffic in an orderly fashion. This prevents backups from slowing things down.
That’s how load balancing works. You’re basically distributing the load evenly across a network of servers so no single server fails trying to accommodate excess traffic. As a result, this strategy ensures that your website’s performance remains stable and reliable — even during rush hour.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) Implementation for Improved Performance
A content delivery network stores a cached version of your content in multiple geographic locations. This setup allows users to access data from the closest server.
As a result, a CDN speeds up the loading time and reduces the load on your primary server. It delivers your cached content to you anytime you load a webpage instead of running to the server to collect the webpage and then running back to you to display its contents.
Caching Mechanisms and Optimization Techniques
Caching involves storing copies of files temporarily to reduce the load on your server and speed up the response time to user requests. I know caching and CDNs may sound similar, but they have unique functions.
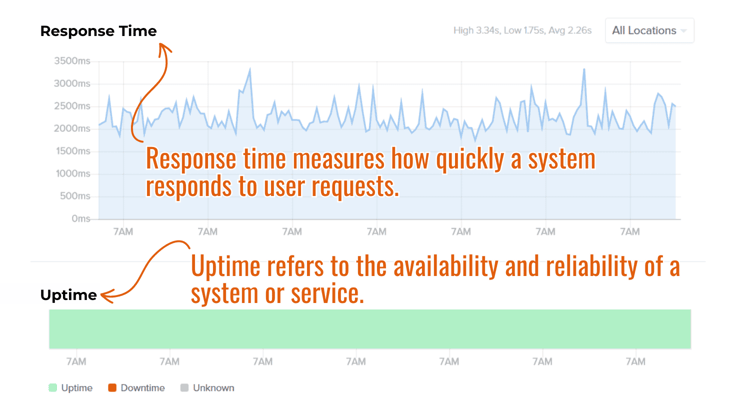
When we say “caching,” we mean the technique or process of storing copies of files in temporary storage. This process can happen both at the browser and server level. A CDN is a network of servers where server caching actually happens. Notice the difference between these two? One is a process, and the other is a physical technology.
Scalability Planning to Manage Traffic Spikes
You need to plan for scalability in order to handle sudden increases in web traffic without compromising uptime. This planning process involves setting up your infrastructure to dynamically adjust and scale resources based on real-time demands.
Whether through elastic cloud solutions like cloud hosting or on-demand resource allocation, preparing for traffic spikes is a great way to make sure that your website remains operational and efficient under varying load conditions.
Real-World Examples
Perhaps one of the best ways to understand and appreciate the importance of uptime is by looking at real-world examples and case studies of websites with high uptime rates. Below, we’ll explore Google.com and YouTube.com, the top two most visited websites in the world.
Google.com: 100% Uptime

Google.com receives about 164 billion monthly visitors, earning itself the title of the world’s most visited website.
Aside from being a search engine, part of the reason Google continues to command such a high number of monthly visitors is its high uptime.
It all boils down to its powerful cloud hosting infrastructure, which it continually improves on.
For context, the tech behemoth plans to invest up to $50 billion in artificial intelligence and cloud hosting infrastructure.
YouTube.com: 100% Uptime

Have you ever wondered why YouTube is rarely down? Part of the reason is that Google owns YouTube.
We’ve already seen how powerful Google’s hosting infrastructure is. That explains why YouTube comfortably handles more than 110 billion monthly visitors consistently without downtime.
Today, YouTube.com is the second-most visited website in the world.
Take a Proactive Approach to Uptime Management
Uptime is something you can’t ignore when choosing a web hosting provider. It can have a huge impact — positive or negative — on your business’s success. Poor uptime can even influence your site’s performance in search engine rankings and drive your site visitors to your competition.
To avoid the headache of downtime, find a host that offers 99.9% uptime or more. Highly redundant infrastructure, such as cloud hosting, can give you even higher uptime percentages. Once you’ve found a provider, you should conduct regular uptime monitoring using the tools I recommended earlier.
If you use the right monitoring tools and implement a CDN and caching strategy, your website’s performance will take off.







