
What is VPS hosting, you may ask — and where does it fit among all the web hosting options out there? Well, many know the housing analogy when talking about web hosting: Shared hosting is renting an apartment, VPS is like owning a condo, and dedicated servers are equivalent to owning your own home. We’ve used the comparison plenty, but it’s time for something new.
Fresh off discovering and using Pizza-as-a-Service to describe cloud service models, we’re ready to compare all things web hosting to pizza. Quickly, VPS stands for virtual private server and resides between shared and dedicated plans on the hosting spectrum. When it comes to pizza (as all things inevitably do), VPS equates to splitting a pizza with a friend and choosing the specific toppings you want on each half.
Let’s take a look at the top hosts and services we recommend before I define VPS hosting and outline its delicious, cheesy advantages.
1. What are the Best VPS Hosting Services? (Top 3)
When you’re ready to upgrade your hosting to a VPS plan, see if your current host offers the service. If you listened to us and signed up with one of our top shared hosting providers, chances are the company will migrate your websites, applications, and files to a VPS plan for free.
Otherwise, take a look at our three favorite VPS providers below. When shopping around, pay attention to which companies offer more powerful and speedy SSD storage, redundant and scalable cloud infrastructure, managed patches and updates, and instantaneous provisioning.
1. Hostinger.com
- Cloud-based SSD storage for speed and reliability
- Double your RAM with burst periods
- FREE dedicated IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
- Custom control panel for reboots and OS installs
- HostingAdvice readers enjoy more than 50% off
- Get started on Hostinger now.
VPS
RATING
★★★★★
Our Review
Hostinger's laser focus on providing affordable hosting solutions shines brightest with the company's VPS packages. The company provides six different virtual server plans, including one that costs less than $5. Go to full review »
| Setup Time | Disk Space | CPU | RAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 minutes | 50 GB NVMe - 400 GB NVMe | 1 - 8 cores | 4 GB - 32 GB |
2. Kamatera.com
- Cloud VPS that's more flexible and affordable
- Load balancer, firewall, and managed services
- Premium Intel CPUs with 300% more power
- Choose between monthly or hourly billing
- Sign up today for a 30-day FREE trial
- Get started on Kamatera now.
VPS
RATING
★★★★★
Our Review
Backed by cutting-edge cloud computing technology, Kamatera adds instant and limitless scalability to the VPS hosting marketplace. Each cloud or virtual server is equipped with blazing-fast SSD storage and Intel Xeon Platinum CPUs. Go to full review »
| Setup Time | Disk Space | CPU | RAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 minutes | 20 GB SSD - 4 TB SSD | 1 - 32 cores | 1 GB - 128 GB |
3. A2Hosting.com
- Turbo server & cache options for faster page loads
- Well-built plans starting with 4GB RAM
- FREE CDN plus auto-installs with Softaculous
- Multilingual support and up to unlimited databases
- Enhanced security with and daily kernel updates
- Get started on A2 Hosting now.
VPS
RATING
★★★★★
Our Review
While A2 Hosting's turbocharged shared hosting platform gives site owners ample room to grow, the company's tech prowess is on full display with its portfolio of VPS options. Ranging from unmanaged, bare-metal environments to stress-free, fully managed space, A2 Hosting is sure to have the perfect option for your expanding online presence. Go to full review »
| Setup Time | Disk Space | CPU | RAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 minutes | 20 GB SSD - 450 GB SSD | 1 - 10 cores | 1 GB - 32 GB |
2. What Does VPS Hosting Mean?
When it comes to the different types of hosting plans available, you can think of shared hosting as that already made, cheap pizza you get to share with seven or eight friends — there’s little say on the toppings and you’ll only get a slice or two, even if your growling stomach demands more.
With VPS hosting, you and another person can choose from higher quality ingredients and decide if the pineapple, for example, should only go on part of the pizza. Dedicated hosting, on the other hand, likens to skipping the delivery menu in favor of making your own and not sharing with anyone else. You have total control over how your pizza tastes, even though someone else might cook the pie in their oven.
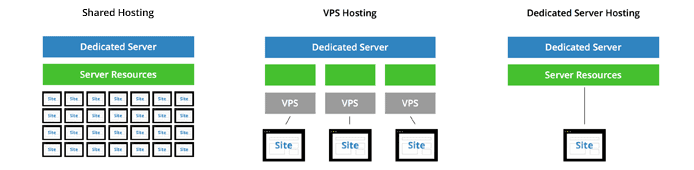
VPS hosting offers customers more resources and flexibility without investing in a dedicated server.
In VPS hosting, a server has been divided into virtualized partitions or virtual machines. You have more control and computing resources than shared hosting packages (in other words, more pizza to satisfy your growing appetite) but still share the hardware with other VPS customers while your traffic grows to the point where a dedicated server makes the most financial and performance sense.
A VPS runs its own operating system copy and acts as an independent dedicated server, even though the physical server might contain several virtual environments. Users have administrative rights to their VPS and can install their own instances of various applications, including Apache, PHP, or MySQL.
3. What is “Cloud” VPS Hosting?
As with all these hosting analogies, cloud hosting makes things a bit more hazy and difficult to explain. Returning to pizza, cloud VPS hosting is roughly akin to eating at an affordable pizza buffet. You can take slices from several different types of pizzas and go back up to the buffet for more if or when you’re hungry.
A cloud-based VPS still draws resources from a virtual machine, but the environment is made up of several different servers clustered or networked together. Each cloud server helps conduct a particular set of tasks, and other servers are ready to fill in in the event that something fails or crashes. This makes cloud VPS hosting extremely performant, scalable, and reliable.
For the pizza analogy to truly apply, however, we have to make a few strange tweaks. Most cloud VPS hosting plans adopt a pay-as-you-go model, billing customers for exactly the computing or storage resources used. So, cloud VPS is totally like eating at a pizza buffet — that is, if you’re visiting one that charges you by the slice and lets you put the uneaten pizza back on the buffet. Regardless, be sure to check out our three favorite cloud VPS hosting providers:
1. Kamatera.com
- Ultimate scalability with limitless customizations
- Create and deploy servers in 60 seconds
- Easily add load balancers and firewalls
- Stellar 99.95% uptime guarantee
- Sign up today for a 30-day FREE trial
- Get started on Kamatera now.
CLOUD
RATING
★★★★★
Our Review
Starting with more than 60 operating system images to choose from, Kamatera is a strong option for developers who know exactly what environment works best for their project. Customize your cloud server as needed and deploy in less than a minute. Go to full review »
| Setup Time | Disk Space | CPU | RAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 minutes | 20 GB SSD - 4 TB SSD | 1 - 32 cores | 1 GB - 128 GB |
2. IONOS.com
- Start with $100 in credit for your first month
- Auto scaling with premium Intel processors
- Customized operating systems (Linux or Windows)
- Deploy Linux instances in less than 1 minute
- Transparent costs and by-the-minute billing
- Get started on 1&1 IONOS now.
CLOUD
RATING
★★★★★
Our Review
Boasting 99. 998% platform availability, the popular cloud hosting services from 1&1 IONOS deploy more than 2,500 virtual machines each week. Go to full review »
| Setup Time | Disk Space | CPU | RAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 minutes | 10 GB NVMe - 640 GB NVMe | 1 - 24 cores | 512 MB.- 48 GB |
3. Cloudways.com
- Managed cloud hosting with 24/7/365 monitoring
- Choose from 5 popular cloud providers
- Auto-healing cloud servers with FREE backups
- 3-day free trial with no credit card required
- Host unlimited apps with no contract lock-in
- Get started on Cloudways now.
CLOUD
RATING
★★★★★
Our Review
If you can’t beat the cloud provider behemoths, offer their infrastructure as a service. Cloudways gives customers their choice of cloud platform: AWS, Google, Linode, Digital Ocean, or Vultr. Go to full review »
| Setup Time | Disk Space | CPU | RAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 minutes | 20 GB SSD - 4 TB SSD | 1 - 96 cores | 1 GB - 384 GB |
4. What are the Advantages and How Much Does It Cost?
Jumping from a shared hosting plan into a VPS unlocks a bevy of new functionalities. Being able to configure your environment through full root access is a major perk of VPS hosting, along with the noticeable boosts in performance and stability because fewer customers share the computing resources.
If the added technical responsibility intimidates you, however, many hosting providers begin offering managed services at the VPS level. That means the company’s in-house experts and support staff will handle everything from server setups and software installation to platform optimization and enhanced security. Your host will take care of maintaining and updating the infrastructure so you can focus on your company, application, or website.

Many VPS hosting providers offer managed services such as security patches or operating system updates.
Because of the upgraded features, resources, and support, VPS hosting plans are understandably more expensive than shared hosting. However, that doesn’t mean VPS is cost-prohibitive or that you can’t find good services for great, affordable prices. Simple, bare-bones VPS plans from respected, reputable hosting providers typically start out around $30 per month — though many of our favorite VPS hosts allow us to give you a discount.
As you add computing resources and servers to your VPS cluster, however, expect those prices to grow. Another big benefit of VPS hosting, especially of the cloud flavor, is the ability to quickly scale your infrastructure to meet traffic demands. You can add or remove servers, often in an automated fashion, with a click or two of the mouse and only pay for what you use.
5. What is VPS Hosting Used For and Who Needs It?
VPS hosting is the service of choice for small or medium businessessmall or medium businesses looking for more control, flexibility, and performance than shared hosting but without the investment required to move all the way up to a dedicated server. While everyone from baffled first-time website owners to seasoned individual developers populates the shared hosting customer ranks, VPS users typically have professional-level experience or critical business needs from their web hosting.
Availability, security, and speed are all critically important to businesses. VPS hosting plans deliver that and more, often automating routine processes, including security monitoring and load balancing, and booting up additional servers and computing resources. Although setting up your VPS infrastructure and processes can be quite a bit more intense (or not, if you have a managed hosting plan), the automation and added services from VPS packages often make customers’ experiences resemble shared hosting’s “set it and forget it” routine.
So, How Can a Virtual Server Help Scale Your Business?
Just as pizza chefs toss the dough in the air to extend it, VPS hosting plans can elevate your business to new heights. As you move forward (hopefully with one of our recommended hosts), we hope your VPS hosting adventures will be as exciting and delicious as stumbling upon a late-night pizza joint serving hot, fresh slices of buffalo chicken pizza.
With a larger administrative role over your hosting environment, you can ensure your virtual private server is perfectly tailored to your website or application’s needs. Top-notch performance and security will boost your brand’s trustworthiness among potential consumers.
Top-notch ingredients, such as scalability, redundant cloud infrastructure, ultimate flexibility, and pay-as-you-go billing, give you a taste of the benefits a VPS host can deliver.
HostingAdvice.com is a free online resource that offers valuable content and comparison services to users. To keep this resource 100% free, we receive compensation from many of the offers listed on the site. Along with key review factors, this compensation may impact how and where products appear across the site (including, for example, the order in which they appear). HostingAdvice.com does not include the entire universe of available offers. Editorial opinions expressed on the site are strictly our own and are not provided, endorsed, or approved by advertisers.
Our site is committed to publishing independent, accurate content guided by strict editorial guidelines. Before articles and reviews are published on our site, they undergo a thorough review process performed by a team of independent editors and subject-matter experts to ensure the content’s accuracy, timeliness, and impartiality. Our editorial team is separate and independent of our site’s advertisers, and the opinions they express on our site are their own. To read more about our team members and their editorial backgrounds, please visit our site’s About page.









